Beyond Standards: Defining Professional Medical Display Solutions: Atemitech Partners with Global Brands to Co-Create Diagnostic-Grade Terminals
February 10, 2026
With the passing of the EU's **Batteries and Waste Batteries Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2023/1542)** in 2023, the design of electronic products such as laptops is facing new regulatory challenges. This regulation, which requires consumers to be able to **self-disassemble and replace batteries starting from 2027**, has sent shockwaves through the industry and significantly impacted mechanical design.
How to Design Removable Batteries to Comply with the EU Battery Regulation (EU) 2023/1542?
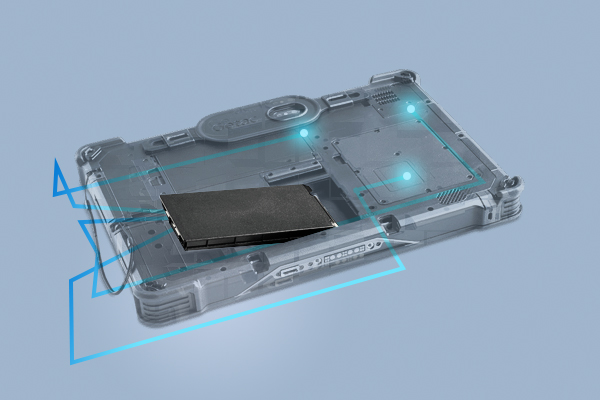
In the past, consumers could typically only add hard drives or memory after purchasing a laptop. The battery was a component hidden under layers of mechanical structure, and if there were issues or if it needed to be scrapped, it had to be sent back to a collaborating vendor for disassembly according to SOPs. However, with the regulation passed, we must consider incorporating the following key points when designing **removable battery structures**:
1. Non-Destructive Disassembly Mechanism
The regulation explicitly states that users **should not need special tools or cause product damage** when replacing the battery. Therefore, the structural design needs to be adjusted to include:
- Using **screws or snap-fit structures**, avoiding strong glues or adhesives.
- **Reserving space for disassembly and force application points** for tools.
- To protect the main body, the battery module should be replaceable **without removing the motherboard**.
2. Integration of Modular Design
In response to the removable design, the battery module should be changed to an **independent unit** for easy replacement and recycling. Considering production and user repair, the following are suggested:
• The battery and the main board should use a **detachable connection** (such as FPC or pin plug-in).
• **Reserving fixing points and mistake-proofing structures** to prevent incorrect operation.
• **Optimizing module size and shape** to facilitate production and assembly, as overly thin or long designs can easily cause deformation.
3. Labeling and Identification
According to the regulation, the battery module needs to be marked with **specifications and recyclable information**, which includes reserving a **clear labeling area** (such as model, capacity, recycling icon), using **scratch-resistant and high-temperature resistant printing or laser marking** for materials, and finally, providing **clear disassembly/assembly graphical instructions** for user reference.
4. Considerations for ESG and the Circular Economy
In fact, modifying the structural design early is not just to comply with regulations, but also to prepare for **corporate sustainable development (ESG)**. When we reduce the use of single-use adhesives and the battery module can be completely disassembled, sorted, and recycled, it benefits the company's promotion of **material and product carbon footprint**, and is more aligned with **green supply chain goals**.
How **HanTong Technology** Responds to the Requirements of the EU Battery Regulation (EU) 2023/1542:
We provide **structural design consultation and module validation services** in response to the EU Battery Regulation, including:
- Design drawings and animation for disassembly/assembly procedures
- Module replaceability testing and component lifespan evaluation
- Development of compliant labeling, structure, and mistake-proofing (Poka-Yoke) designs
Since 2023, we have assisted our OEM clients, specifically a European brand, in completing the design and integration of a modular removable battery structure that complies with EU 2023/1542. This support helped the client successfully pass compliance audits and receive positive feedback from users.